PATELLO FEMORAL PAIN SYNDROME
Introduction
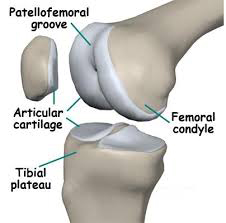
PFPS/patella femoral pain syndrome is terminology used for pain around the knee cap or front of the knee. Also known as anterior knee pain, patella mal-tracking, chondromalacia patella. The patella is covered with a layer of smooth cartilage, which normally glides across the knee when the joint is bent.
The pain is caused by rubbing of the undersurface of the patella/knee cap against femoral trochlea/thigh bone, irritating the cartilage surface.
Causes
- Activities such as running, squatting and climbing up and down stairs
- Knock knee deformities
- Female gender
- Flat foot
- Overuse or sudden increase in physical activity
- Patellar instability
- Quadriceps muscle weakness
- Sudden weight gain as during pregnancy
Symptoms
- Pain – can be anywhere around the knee, sometimes both knees can be involved
- Clicking or clunking
- Mild swelling
- Instability
- Pain can be while squatting, sitting crosslegged, sittiing for long hours as in during watching movies or travelling
Normal knee
Mal alignment

Investigations
X-ray In different positions of the knee to analyse anatomical variations, position of the knee cap.
Scannogram to assess anatomical and mechanical axis
MRI to assess the quality of cartilage of the knee cap and associated pathological findings
CT scans to know the relation ship of patella to the trochlea
Treatment
Non-surgical treatment
Most of the patients get better with non-surgical treatment
- Analgesics
- Modification of activities
- Shoe inserts to correct the foot posture may help
- Structured physical therapy to condition and strengthen the muscles
- Stretches
- Strengthening
- Balance exercises
- Core stability exercises for spine and pelvis
- Plyometrics in athletes
Occasionally your symptoms may increase when physical therapy is started, you may not experience benefits out of it for at least 2 to 3 months, hence it is important not to discontinue in-between.
Surgical treatment
Indications
- Gross structural deformities with alignment
- Gross foot deformities
- Excessive patellar tilt and displacement
- Patellar instability
- Grade 3 and grade 4 chondromalacia
Techniques
- Arthroscopic chondroplasty and bio stimulation procedures Deformity corrections
- Open bony procedures




Follow us